In brief⚡
Events Under the Spotlight💥
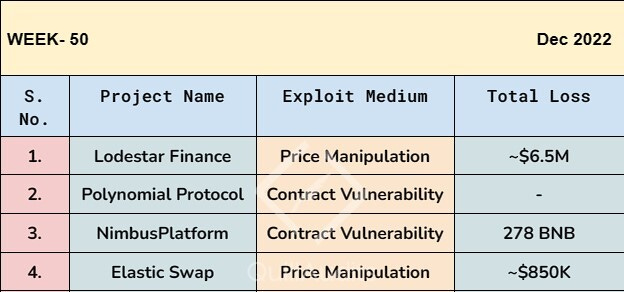
Lodestar Finance Arbitrum-Based Defi Protocol Hacked for ~$6.5 Million.
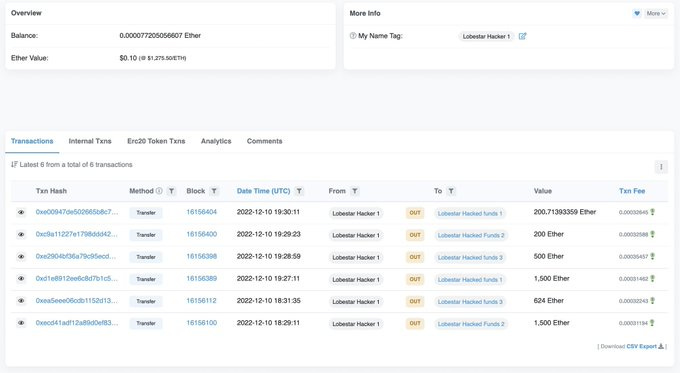
On December 10, 2022, the arbitral-based lending platform Lodestar Finance was used. According to community reports, Lodestar lost approximately $6.9 million due to the vulnerability.
The hacker manipulated the plvGLP contract's exchange rate before supplying plvGLP collateral to Lodestar and borrowing all available liquidity.
This enabled the exploiter to withdraw "what they could." However, a "collateralization ratio mechanism prevented them from fully cashing out the plvGLP," according to the report.
Lodestar's total value locked (TVL) was reduced from nearly $7 million to $11.06. Lodestar (LODE), the project's native cryptocurrency, has lost 53% of its value against the US dollar.
Polynomial Protocol was exploited due to optimism's deposit contract flaw.
Polynomial Protocol exploits a flaw in optimism's deposit contract.
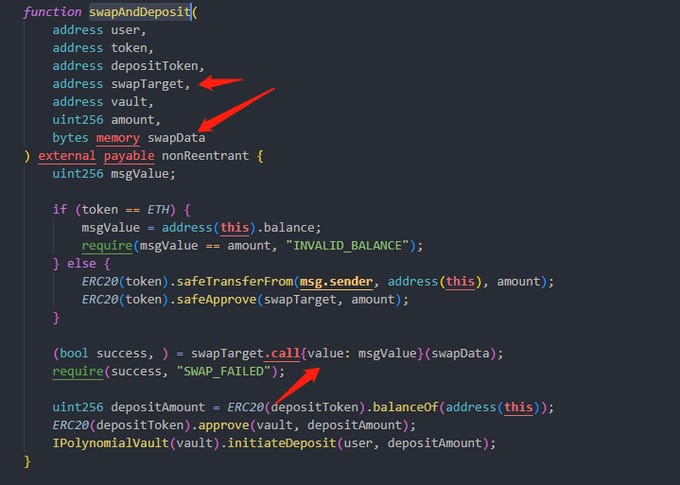
The attacker deployed a contract to batch-steal USDC.
Attack Contract Address:
0xf682e302f16c9509ffa133029ccf6de55f4e29a8The issue stems from the
swapAndDeposit()function, which has no input restrictions.Anyone with an address can enter it and maliciously construct swapData to steal contract-approved tokens.
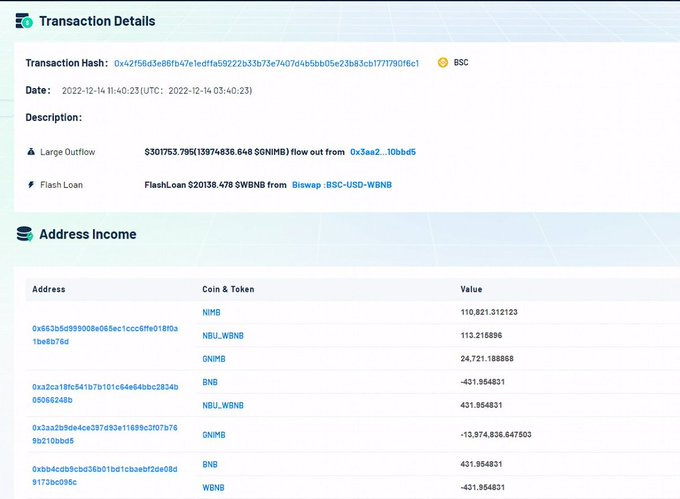
NimbusPlatform suffered a loss of 278BNB due to contract vulnerability
The NimbusPlatform project on the BSC chain was targeted, and the attacker profited by approximately 278 BNB.
The main reason for this attack is that the calculation of rewards only depends on the number of tokens in the pool, which allows flash loans to be manipulated, resulting in more rewards than expected.
ElasticSwap project on $AVAX has exploited for ~$850K.
The abuse of two accounting systems was the root cause of the price manipulation attack.
Its calculation methods for adding and removing liquidity from contracts needed more consistency. The added liquidity is calculated using a constant K value algorithm, whereas the removed liquidity is calculated using the balance of two tokens in the current pool.
The attacker first adds liquidity to the TIC-USDC pool by transferring a certain amount of $USDC.e, after which the amount of USDC.e to be transferred to the attacker is multiplied by the number of LP tokens. Finally, the attacker drains liquidity to profit.